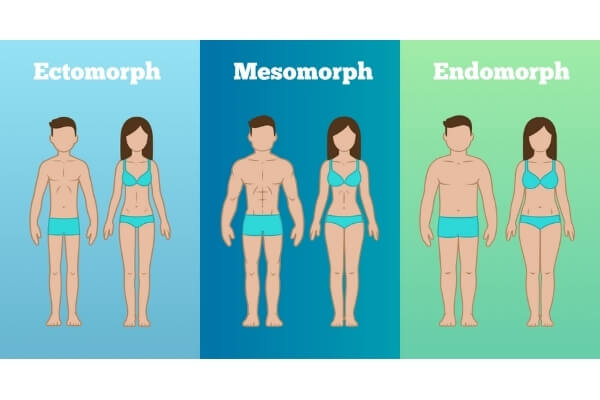
What is your body type?
Body type — whether ecto, meso, or endomorph — can determine what sports suit you best, as well as what you should be eating to fuel your activities. Yes, it’s true — those darn ectos can get away with a little extra pasta!
WHAT IS EATING FOR YOUR BODY TYPE?
Many people think that “body type” just describes the way someone looks. In fact, your body type can also provide information about how you respond to food intake and about your hormonal and sympathetic nervous system (SNS) characteristics.
Physique characteristics can thus be linked to metabolic differences between individuals. Once someone establishes their body type, they can then adjust nutrient intake to maximize body composition and health related goals.
There are three general categories of body types (somatotypes): ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph.
Very few people fall perfectly into one of the three categories. People are often a mix of characteristics. Additionally, years of training and good nutrition can change the outward appearance of one’s body.
For instance, a bodybuilder might be mistaken for a “natural” mesomorph when in fact, s/he is really an endomorph who’s trained and dieted hard; or an ectomorph who’s spent years guzzling protein shakes and doing the power lifts.
An ectomorph who’s gained a little weight around the middle from a sedentary lifestyle and poor nutrition might assume they’re more endomorphic.
However, most people can find their general tendencies in one of the three groups.
Ectomorphs are thin individuals characterized by smaller bone structures and thinner limbs. Think of a typical endurance athlete. They tend to be thyroid and SNS dominant with either a higher output or higher sensitivity to catecholamines like epinephrine and norepinephrine. This profile is linked to a fast metabolic rate and a high carbohydrate tolerance.
This group generally does best with more carbohydrates in the diet, along with a moderate protein and lower fat intake. A nutrient distribution for this body type might be around 55% carbs, 25% protein, and 20% fat.
Mesomorphs have a medium sized bone structure and athletic body, and if they’re active, they usually have a considerable amount of lean mass. Many explosive athletes like wrestlers and gymnasts fit these criteria. Mesomorphs tend to be testosterone and growth hormone dominant. This profile leads to a predisposition for muscle gain and the maintenance of a lower body fat.
Mesomorphs typically do best on a mixed diet, consisting of balanced carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. A macronutrient split of 40% carbohydrate, 30% protein, and 30% fat can work well.
Endomorphs have a larger bone structure with higher amounts of total body mass and fat mass. Football lineman and powerlifters are frequently endomorphs. They tend to be naturally less active. Where the ectomorphs tend to burn off excess calories with near constant movement, excess calories in endomorphs do not seem to cause that same increase in expenditure. This means that excess calories are more likely to be stored as fat. This profile leads to a greater propensity for energy storage, including both lean mass and fat mass. This can also mean a lower carbohydrate tolerance.
Endomorphs typically do best on a higher fat and protein intake with carbohydrate intake being controlled and properly timed (e.g., after exercise). So that’s what we recommend: more fat and protein, less carbohydrate.